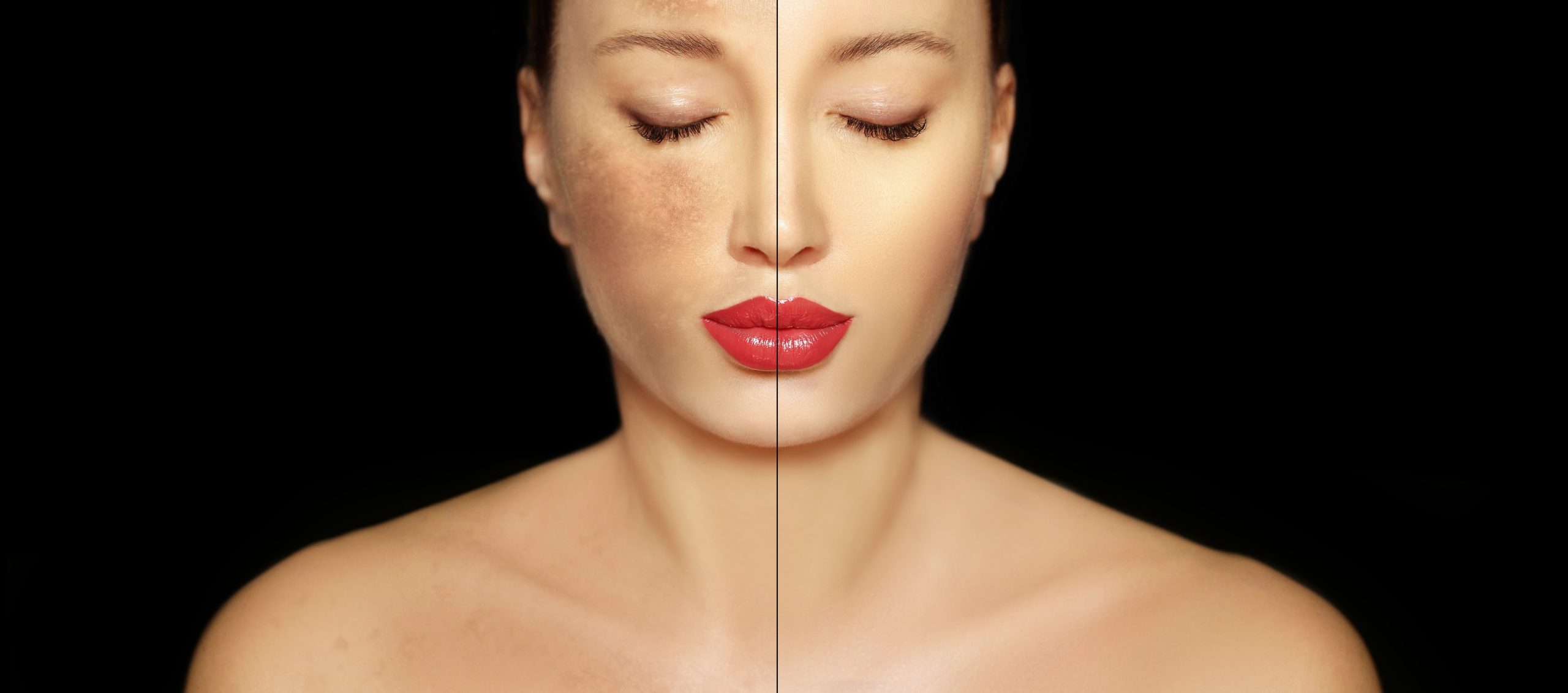
Melasma is a skin condition that causes patches and spots, usually on the face, which are darker than your natural skin tone. While common, melasma can be mistaken for another skin condition. Board-certified dermatologists have the expertise required to give you an accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment plan.


Questions and Answers
at is the main cause of melasma?
Wh What causes melasma? There are two main causes of melasma: radiation, whether ultraviolet, visible light, or infrared (heat) light; and hormones. Ultraviolet and infrared radiation from the sun are key in making melasma worse
How do I get rid of melasma?
The most commonly used treatments for melasma are skin lightening medications that are applied topically. These include medications such as hydroquinone, azelaic acid, kojic acid, niacinamide, cysteamine, rucinol, and tranexamic acid.
What are 3 different types of melasma?
Historically, melasma has been classified as having three histologic variants: epidermal, dermal, and mixed
What deficiency causes melasma?
While melasma most often develops after prolonged sun exposure or during pregnancy due to fluctuating hormone levels, it may also be a sign of malnutrition or liver disease. Studies have linked melasma to people with poor liver function, vitamin B12 deficiency and iron
What foods trigger melasma?
So, when you want to eat something to treat melasma and freckles, eliminate suspected allergenic foods such as eggs, milk and dairy products, soy and soy products, wheat gluten, marine fish and shellfish, peanuts. For many people, melasma and freckles are hormonal triggers.
What should you avoid with melasma?
Do this by avoiding the sun, tanning beds, LED screens, irritating soaps and birth control that includes hormones. If you are exposed to the sun, be sure to wear sunscreen with iron oxides and a SPF of 30-50 applied every two hours, as well as a wide-brimmed hat. These steps may prevent your melasma from getting worse.
What is the fastest way to cure melasma naturally?
Treatment procedures may help
If your melasma does not improve with topical or oral medications, adding procedures such as chemical peels and laser therapies to a treatment regimen could be beneficial.
Chemical peels use substances like glycolic acid, alpha-hydroxy acids, and salicylic acid to remove the superficial layer of the skin that contains excess pigment in melasma patients. The effects of a chemical peel are temporary, since this procedure removes a layer of skin without reducing the production of pigment in regenerating deeper layers.
Laser therapies can destroy pigment cells in skin and therefore lighten the dark spots in melasma. However, as with any other treatment option for melasma, there is considerable risk of relapse post-treatment.

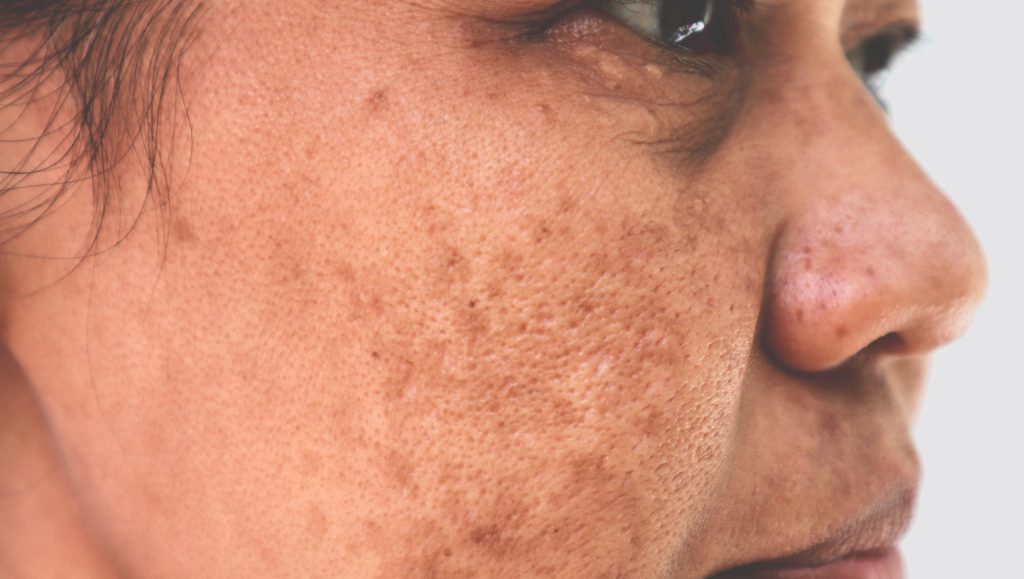
Maintenance therapy and prevention
After achieving improvement of melasma lesions, strict sun protection and maintenance therapy need to be continued. Skin lighteners other than hydroquinone can be used in combination with retinoids to maintain the results, and hydroquinone therapy may be used intermittently if needed.

